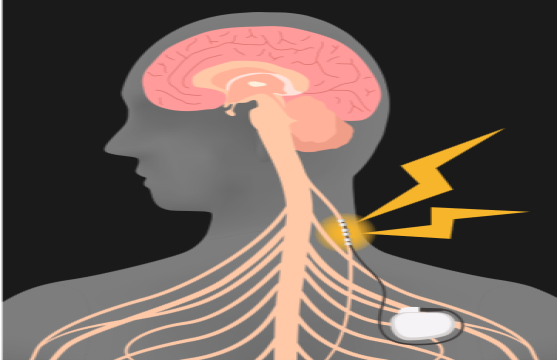
A small electrical device, like a pacemaker, is placed under the skin on the chest. From it a wire goes under the skin and connects to the vagus nerve, which is a nerve in the neck. Bursts of electricity go along the wire to the nerve to help make seizures less regular and less severe. When the electrical signal is happening, every five minutes for 30 seconds, you may have a hoarse voice, a sore throat and a cough. The battery of the VNS will need to be replaced about every 10 years.
Other Epilepsy Treatments
Vagus nerve stimulation (VNS)
Deep brain stimulation (DBS)
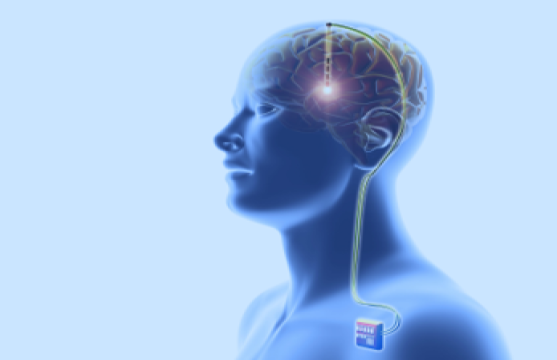
Like VNS but the wires are run under the skin into the brain, the electrical signals change the electrical signals in the brain. This is still a new procedure and its effectiveness for treating epilepsy is not known yet. There are some serious side effects too including bleeding on the brain, depression and memory problems.
If your doctor suggests DBS, then make sure you go through the side effects with them and make sure it is the right option for you.
Diet

A ketogenic diet is high in fats and lower in protein and carbohydrates. It is recommended as an option for children to help control their seizures if anti-epileptic drugs (AEDs) are not working by changing the levels of chemicals in the brain. This diet is only really recommended for children as a high fat diet can lead to diabetes or cardiovascular disease in adults. A dietician will help you develop a diet plan.
Complementary therapies

An epilepsy specialist will offer you advice if you are considering alternative therapies as stopping AEDs can cause seizures. Some herbal remedies interact with epilepsy medicines to stop them working properly, an example of this is St John’s Wort. If stress is a trigger for your epilepsy then relaxation therapies, yoga or meditation may help you.
Send your Feedback!
Would you recommend the UCBCares website to other visitors?